Zürcher Kantonalbank: Pioneer in biodiversity
Companies that are committed to preserving and regenerating biodiversity make an important contribution to environmental protection. At the same time, they improve their profitability. With this in mind, we are breaking new ground together with ESG specialist Sustainalytics.
Text: Rocchino Contangelo

Zürcher Kantonalbank is pioneering the field of biodiversity. Together with renowned ESG service provider Sustainalytics, we define relevant key indicators for biodiversity1. The key indicators are intended to help find companies that preserve and restore biodiversity.
Biodiversity engagement: commitment and measurability
In a first phase of this engagement, we enter into dialogue with listed companies. Our ESG research team focuses on the following points:
- Raising awareness of the topic and its urgency
- Obtaining commitments from companies
- Defining goals to be achieved
In order to measure the impact of companies on biodiversity and track the progress of the engagement, the following metrics can be used (still being finalised):
- A company's annual impact on global biodiversity
- Lifecycle assessments of water, land use and ecosystems
- Biodiversity footprint of economic activity with a value chain approach
The fundamental work and principles of the Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosure (TNFD) serve as a guideline for the commitment to biodiversity. Zürcher Kantonalbank is a member of the TNFD and provides its expertise for reviewing the fundamental work and principles.
Connection between biodiversity and climate change
Since 1960, the rate of extinction caused by humans has significantly exceeded the natural rate. The pressure on biodiversity can be attributed, among other things, to intensive agriculture, increasing urbanisation, the loss of natural land for example due to housing on green areas, or increasing forestry with predominantly one single tree species. It is also feared that the effects of climate change on forests could occur to a degree that makes natural adaptation through genetic processes or species migration more difficult.
Biodiversity protection supports the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as the fight against poverty (SDG 1), food security (SDG 2), health protection (SDG 3) and the preservation of drinking water, underwater life and terrestrial ecosystems (SDGs 6, 14 and 15).
Switzerland offers potential
However, measured against the Aichi Biodiversity Targets, countries have so far failed miserably in terms of protecting biodiversity. According to an analysis of several domestic environmental associations, Switzerland has only achieved one of the 18 defined strategic goals from 2012, namely for forest management. In 2017, the Federal Council approved and launched the action plan for the «Strategy on Biodiversity Switzerland.»
Biodiversity is affected by multiple factors and encompasses several dimensions and fields for action (see chart below). This makes it all the more urgent to consider and implement biodiversity conservation in a holistic manner.
Measures to reduce and restore biodiversity
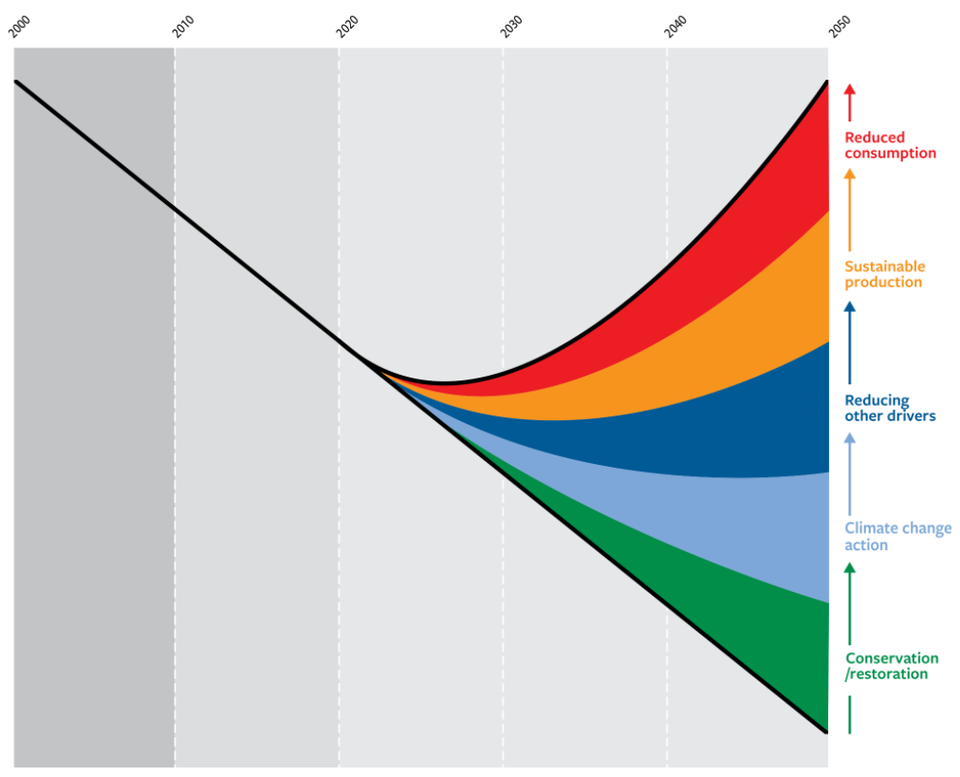
Biodiversity has been declining for several years. A further decline is very likely if no counteracting measures are taken, as can be seen in the chart. The following measures could reduce the rate of biodiversity loss and, when optimally combined, even restore biodiversity after 2030. These are (from bottom to top):
- Consistent protection and restoration of ecosystems
- Slowdown of climate change
- Measures against pollution, invasive species and over-use
- More sustainable production of goods and services, in particular food
- Reduction of consumption and waste
The efficient and effective protection of biodiversity and its restoration requires a large number of active participants. In light of this, Zürcher Kantonalbank hopes that more competitors get involved.
1 According to the Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN), biodiversity includes «... the diversity of species of animals, plants, fungi and microorganisms, the genetic diversity within the various species, the diversity of habitats and the interactions within and between these dimensions.» (FOEN, 2017)
